Introduction
In the modern era of computers and the internet, cyber threats have become one of the biggest concerns for individuals and companies alike. Malware is likely the most familiar of these threats—a catch-all term for a wide range of malicious software that attacks computer systems in an attempt to breach, damage, or take unauthorized control of them. To enjoy a secure digital experience, you first need to know about malware, its types, modes of transmission, and defense mechanisms.
What is Malware ?

Malware, or malicious software, is any computer program or code designed to interfere with, harm, or gain unauthorized access to computer systems, networks, or devices. It is employed by cybercriminals for numerous purposes, such as stealing confidential information, taking over systems, spying on users, and extorting funds.
Types of malware :-
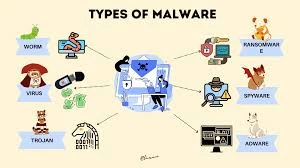
There are a number of malware types, each with its own characteristics and attack techniques. The most prevalent types are listed below:
1. Virus
A computer virus is a form of malware that infects legitimate programs or files and then propagates itself when executed. Viruses can delete or modify data, and they replicate by attachments in emails, file transfers, and downloads.
2. Worms
Worms do not need a host file to propagate, unlike viruses. They infect themselves and propagate over networks, infecting computers without human interaction. Worms may bring networks down, clog systems, and take advantage of security vulnerabilities.
3. Trojans
A Trojan horse (or Trojan) appears to be legitimate software but has malicious code. When installed, it can open backdoors for intruders, steal information, and even hijack the infected computer.
4. Ransomware
Ransomware is a highly malicious type of malware that encrypts a victim’s files and requires payment (ransom) for access restoration. Ransomware frequently is distributed via phishing email and malicious downloads. Publicized ransomware attacks have been waged against hospitals, businesses, and government organizations.
5. Spyware
Spyware is intended to secretly observe user behavior, harvesting sensitive data like login credentials, browsing history, and financial details. Spyware is usually utilized for identity theft and financial fraud.
6. Adware
Adware is malware that produces unwanted ads and leads users to malicious websites. Some adware is harmless, but others have the ability to monitor user activity and subject users to other types of cyber attacks.
7. Rootkits
Rootkits are sophisticated malware applications that burrow deep into the system, which is why they can be tricky to find. Rootkits enable attackers to keep privileged access to infected machines and execute malicious behavior unseen.
8. Keyloggers
A keylogger captures each keystroke input on a system, which makes it possible for attackers to siphon out sensitive data such as usernames, passwords, and credit card information.
How does malware spread ?

Understanding how malware spreads is essential for avoiding infections. Some of the most common techniques of introducing malware into systems are:
- Phishing Emails – Cybercriminals send phishing emails, which contain malicious attachments or links that, when clicked, install malware.
- Malicious Downloads – Downloading files or software from unknown sites may introduce malware onto your system.
- Infected websites – Accessing hacked websites can result in automatic virus downloads (drive-by downloads).
- USB drives and External Devices – Malware can spread through infected USB drives, external hard disks, and memory cards.
- Software Vulnerabilities – Taking advantage of security flaws in outdated software might allow malware to enter systems without the need for user intervention.
- Fake Software Updates – Users are tricked by cybercriminals into downloading counterfeit updates that carry malware.
- Social Media Links – Malicious links presented as trending news or videos can spread malware when opened.
Signs of a Malware Infection :-
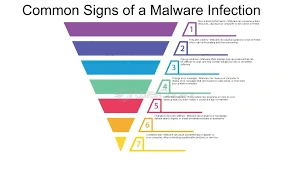
Identifying the signs of a malware infection will enable you to act before extensive damage is done. The typical signs are:
- Slow system performance
- Constant crashes or system errors
- Unusual pop-up advertisements
- Unauthorized settings changes
- Redirecting to unfamiliar websites
- Unexpected data usage or excessive network traffic
- Disabled security software
- Files vanishing or being encrypted
How to protect yourself from malware :-

Malware infections can be prevented by being proactive. Implement these cybersecurity best practices:
- Install Strong Antivirus Software – Install a good antivirus or anti-malware software to scan and delete threats.
- Keep Operating Systems and Software Updated – Update your system regularly to patch security holes.
- Be Careful with Email Attachments and Links – Don’t click on links or download attachments from untrusted sources.
- Use Strong Passwords – Use strong passwords and allow two-factor authentication (2FA) where available.
- Download from Trusted Sources – Do not install software or updates from anywhere else but an official website or a recognized app store.
- Enable a Firewall – A firewall is like a protective wall, blocking malicious traffic from entering your system.
- Regularly Back Up Your Data – Backup important files to avoid data loss during a ransomware attack.
- Don’t Click on Dubious Ads – Avoid click-through ads, as they might have malware.
- Regularly Monitor Your System – Run regular security scans to identify and remove threats.
- Go for Secure Browsing Using a VPN – A Virtual Private Network (VPN) secures your web activity by encrypting it, thus preventing hackers from accessing it.
How to remove Malware :-

If you feel your system has been infected, do the following:
- Disconnect from the Internet – Avoid letting the malware spread or contact remote servers.
- Run a Full System Scan – Scan with your antivirus program for a complete scan.
- Enter Safe Mode – Booting in safe mode will help isolate and delete malware.
- Uninstall Suspicious Programs – Uninstall any new, unfamiliar programs.
- Clear Browser Cache and Extensions – Erase malicious extensions by resetting browser configurations.
- Use Malware Removal Tools – Utilize specialized tools such as Malwarebytes to identify and eliminate sophisticated threats.
- Restore from Backup – Restore from a backup if your files have been affected. This can assist in recovering data.
- Seek Professional Help – If the infection continues, seek help from a cybersecurity professional.
Conclusion :-
Malware is a pervasive and ever-changing threat that can have catastrophic implications for individuals and businesses. By learning about its different types, how it infects, and how to guard against it, you can substantially lower your chances of becoming a victim of cyberattacks. Be cautious, keep your security software current, and practice best methods to have a secure digital life.
By implementing these security precautions, you can protect your devices and your personal data from cyber attacks. Prevention is always better than cure when it comes to cybersecurity.