~ Before knowing about the types of cybercrime, let me tell you an interesting fact of the Cybercrime :-

- Cybercrime will cost the world $10.5 trillion yearly by 2025, marking it as the most massive transfer of economic wealth ever recorded, and surpassing the global drug trade in profit.
- Before discussing the various types of Cybercrime, let’s first understand in short what cybercrime actually means.
~ Definition & Types of cybercrime :
- Cybercrime is one of the illegal actions that use computers or the internet. Some examples of cybercrime include:
- Theft and selling corporate data
- Demand payment to thwart an attack
- Installing viruses in a targeted computer
- Hacking into government or corporate computers
~ Different types of Cybercrime :-

~ Here are some major types of cyber crime these are as follows :-
1. Phishing :

Phishing is a type of social engineering and scam in which attackers trick victims into disclosing confidential information, or installing software like viruses, worms, adware, or ransomware. Phishing attacks have gotten increasingly complex, and they frequently transparently mirror the site being attacked, allowing the attacker to see everything while the victim navigates the site and crosses any further security boundaries with them.
2. Identity theft :-

The term identity theft was firstly introduced in 1964. Identity theft, identity piracy, or identity infringement happens when someone uses another’s personal identifying information, such as their name, identification number, or credit card number, without their consent to perpetrate fraud or other crimes.
3. Malware :-

Malware (a portmanteau of malicious software) is any software that intentionally causes disruption to a computer, server, client, or computer network, leaks private information, gains unauthorized access to information or systems, deprives access to information, or unknowingly interferes with the user’s computer security and privacy.
4. Ransomware :-

Ransomware is a sort of software that encrypts the victim’s personal information until they pay a ransom. They frequently employ difficult-to-trace digital currencies like pay safecard for Bitcoin, as well as other cryptocurrencies, for ransoms, making it tough to track down and prosecute the culprits.
5. Hacking :-

Hacking is typically defined as the act of compromising digital devices and networks by gaining unauthorized access to an account or computer system. Hacking is not always a harmful act, but it is often linked to illicit conduct and data theft by cyber criminals.
6. Cyber espionage :-

Cyber espionage, often known as cyber spying, is a sort of cyberattack in which an unauthorized user seeks to acquire access to sensitive or confidential data or intellectual property (IP) for commercial, competitive, or political purposes.
7. Cyber stalking :-

Cyber stalking occurs when a cyber criminal repeatedly threatens someone over the internet. This crime is frequently committed using email, social media, and other online platforms. Cyber stalking can also occur in conjunction with the more ancient kind of stalking, in which the bad person harasses the victim offline.
8. Computer virus :-

Computer viruses disrupt systems, cause significant operational challenges, and lead to data loss and leakage. They spread across applications and systems by attaching to an executable host file, which triggers their infectious programs when opened. The code then spreads through networks, disks, file-sharing programs, or infected email attachments.
9. Data breaches :-

A Data breach occurs when unauthorized parties gain access to sensitive or confidential information, such as personal data (SSNs, bank account numbers, healthcare data) and corporate data (customer records, intellectual property, and financial information).
10. Software piracy :-

Software piracy is the criminal practice of copying, distributing, altering, selling, or utilizing legally protected software. So, simply put, software piracy is the act of stealing legal software. Software piracy is defined as the illicit copying and use of legal software, and this essential issue has now spread globally.
11. Cyber extortion :-

Cyber extortion occurs when a hacker gains unauthorized access to your organization’s sensitive data or systems and then demands money in exchange for allowing you to restore control or halt the attack. If you have an ecommerce site and a hacker launches a distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) attack, users may be unable to purchase your items or services—at least until you meet the hacker’s demands.
12. Cyber bullying :-

Cyberbullying is defined as bullying through the use of digital technologies. It can happen on social media, chat apps, gaming platforms, and mobile devices. It is repetitive behavior intended to scare, anger, or shame individuals who are targeted.
13. Crypto jacking :-

Cryptojacking is a threat that infiltrates a computer or mobile device and then exploits its resources to mine cryptocurrency. Cryptocurrency is digital or virtual money in the form of tokens or “coins.” The most well-known is Bitcoin, but there are roughly 3,000 other types of cryptocurrency, and while some have entered the physical world via credit cards or other projects, the majority remain virtual.
14. Data theft :-

Data theft is the act of stealing digital information from computers, servers, or electronic devices in order to access personal information or violate privacy. The stolen data can include bank account information, online passwords, passport numbers, driver’s license numbers, social security numbers, medical records, online subscriptions, and so on. Once an unauthorized person gains access to personal or financial information, they can remove, change, or prohibit access without the owner’s permission.
15. DDoS attack :-
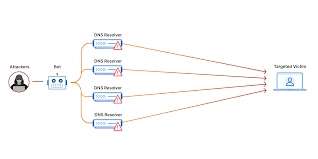
- A distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) attack is a malicious attempt to disrupt the normal traffic of a targeted server, service or network by overwhelming the target or its surrounding infrastructure with a flood of Internet traffic. DDoS attacks achieve effectiveness by utilizing multiple compromised computer systems as sources of attack traffic. Exploited machines can include computers and other networked resources such as loT devices . From a high level, a DDoS attack is like an unexpected traffic jam clogging up the highway, preventing regular traffic from arriving at its destination.
16. DoS attack :-
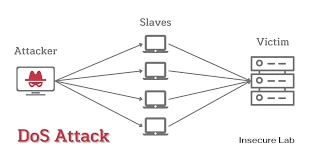
- A denial-of-service (DoS) attack is a sort of cyber attack in which a malicious actor attempts to make a computer or other device unavailable to its intended users by disrupting its usual operation. DoS attacks normally overwhelm or flood a targeted system with requests until they prevent it from processing normal traffic, causing denial-of-service to other users. A single computer launches a DoS attack.